Quantum computers, devices that perform computations by exploiting quantum mechanical phenomena, have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks and optimization problems. In recent years, research teams at both academic institutions and IT companies have been trying to realize this predicted better performance for specific problems, which is broadly known as 'quantum advantage.'
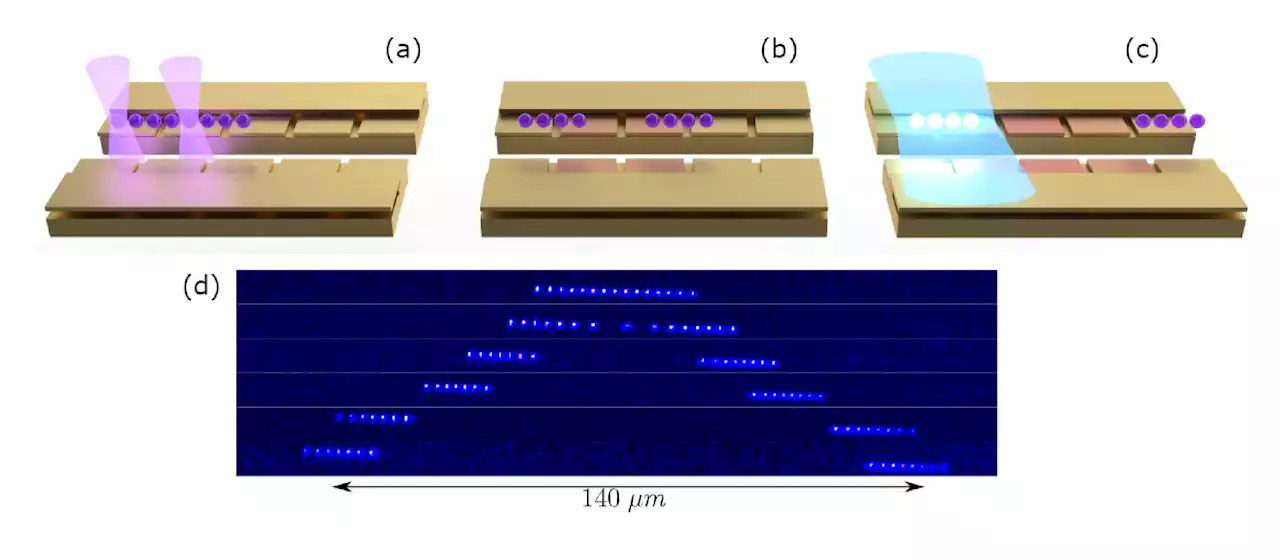
). In their recent study, Zhu's team performed a proof-of-principle demonstration of these protocols, using an ion trap quantum computer."We arranged the qubits into several segments according to their functions throughout the interactive computation," Zhu explained."At each readout stage, we split the target segments apart from the rest of the qubits and shuttle them away to perform readout.
"On one hand, we successfully integrated mid-circuit measurements into arbitrary quantum circuits with sufficiently high overall fidelity using long ion chains," Zhu said."This could be applied to many other interactive algorithms. On the other hand, our demonstration, when suitably scaled to larger systems, promises the efficient verification of quantum computational advantage.
The new protocols introduced and evaluated by this team of researchers has notable advantages over other existing methods to test quantum advantage. For instance, compared to Shor's algorithm, which is also efficiently verifiable, their protocol can be implemented with one order of magnitude fewer quantum gate operations.could be implemented and evaluated in other experiments.
"From a theoretical perspective, we are now interested in applying interactive protocols to other tasks such as certifiable random number generation, remote state preparation and verifying arbitrary quantum computations," Zhu added."Experimentally, using the mid-circuit measurement capability, we are also excited to explore new phenomena, like entanglement phase transitions, as well as the demonstration of coherent feedback protocols, including quantum error correction.
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Quantum computer unveils atomic dynamics of light-sensitive moleculesResearchers have implemented a quantum-based method to observe a quantum effect in the way light-absorbing molecules interact with incoming photons. Known as a conical intersection, the effect puts limitations on the paths molecules can take to change between different configurations. The observation method makes use of a quantum simulator, developed from research in quantum computing, and offers an example of how advances in quantum computing are being used to investigate fundamental science.
Quantum computer unveils atomic dynamics of light-sensitive moleculesResearchers have implemented a quantum-based method to observe a quantum effect in the way light-absorbing molecules interact with incoming photons. Known as a conical intersection, the effect puts limitations on the paths molecules can take to change between different configurations. The observation method makes use of a quantum simulator, developed from research in quantum computing, and offers an example of how advances in quantum computing are being used to investigate fundamental science.
Read more »
 Chessboard-like method enables the operation of largest gate-defined quantum dot systemResearchers from Delft established a way to address many quantum dots with only a few control lines using a chessboard-like method. This enabled the operation of the largest gate-defined quantum dot system ever. Their result is an important step in the development of scalable quantum systems for practical quantum technology. They publish their results in Nature Nanotechnology.
Chessboard-like method enables the operation of largest gate-defined quantum dot systemResearchers from Delft established a way to address many quantum dots with only a few control lines using a chessboard-like method. This enabled the operation of the largest gate-defined quantum dot system ever. Their result is an important step in the development of scalable quantum systems for practical quantum technology. They publish their results in Nature Nanotechnology.
Read more »
 Physicists develop series of quality control tests for quantum computersQuantum technologies—and quantum computers in particular—have the potential to shape the development of technology in the future. Scientists believe that quantum computers will help them solve problems that even the fastest supercomputers are unable to handle yet. Large international IT companies and countries like the United States and China have been making significant investments in the development of this technology. But because quantum computers are based on different laws of physics than conventional computers, laptops, and smartphones, they are more susceptible to malfunction.
Physicists develop series of quality control tests for quantum computersQuantum technologies—and quantum computers in particular—have the potential to shape the development of technology in the future. Scientists believe that quantum computers will help them solve problems that even the fastest supercomputers are unable to handle yet. Large international IT companies and countries like the United States and China have been making significant investments in the development of this technology. But because quantum computers are based on different laws of physics than conventional computers, laptops, and smartphones, they are more susceptible to malfunction.
Read more »
 Quantum computer unveils atomic dynamics of light-sensitive moleculesResearchers at Duke University have implemented a quantum-based method to observe a quantum effect in the way light-absorbing molecules interact with incoming photons. Known as a conical intersection, the effect puts limitations on the paths molecules can take to change between different configurations.
Quantum computer unveils atomic dynamics of light-sensitive moleculesResearchers at Duke University have implemented a quantum-based method to observe a quantum effect in the way light-absorbing molecules interact with incoming photons. Known as a conical intersection, the effect puts limitations on the paths molecules can take to change between different configurations.
Read more »
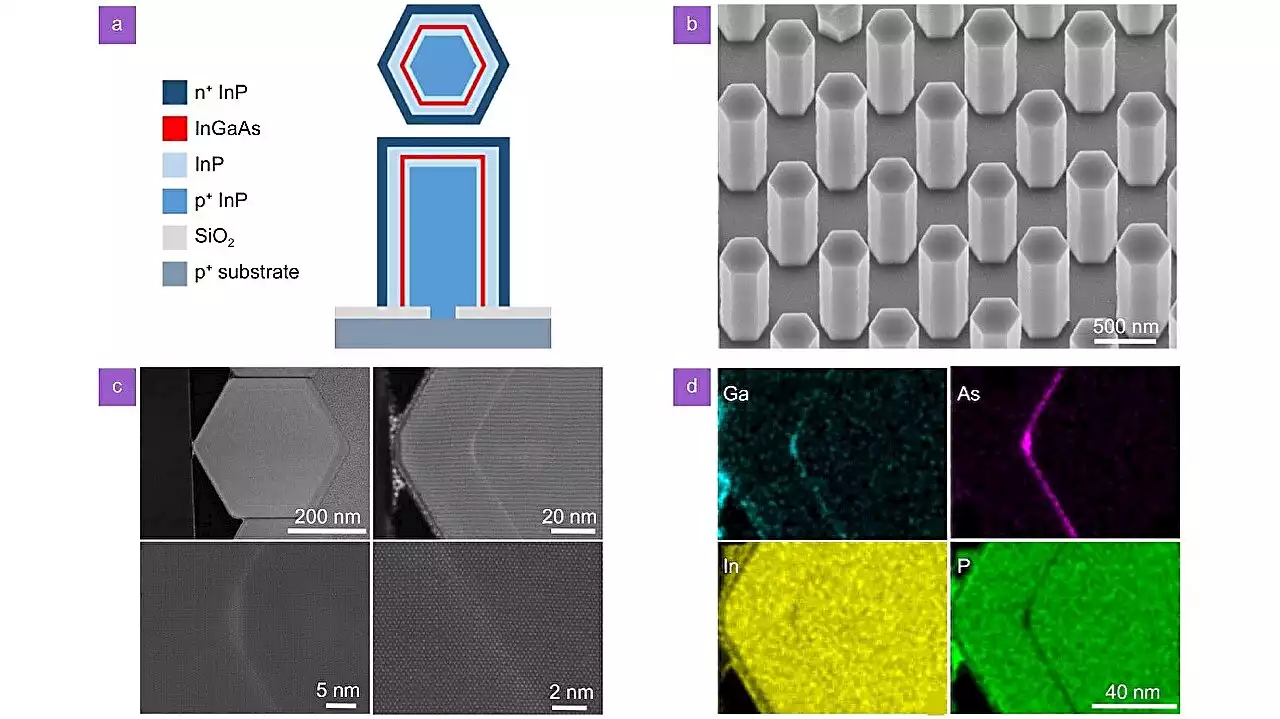 Multiwavelength quantum well nanowire array micro-LED for on-chip optical communicationAs the number of cores in a processor continues to grow, so too does the challenge of connecting them all together. Traditional electrical networks fall short due to latency, limited bandwidth, and high-power consumption. Researchers have long sought for a better alternative, and on-chip nanophotonic systems have emerged as a promising substitute for traditional electrical networks.
Multiwavelength quantum well nanowire array micro-LED for on-chip optical communicationAs the number of cores in a processor continues to grow, so too does the challenge of connecting them all together. Traditional electrical networks fall short due to latency, limited bandwidth, and high-power consumption. Researchers have long sought for a better alternative, and on-chip nanophotonic systems have emerged as a promising substitute for traditional electrical networks.
Read more »
 Scientists use quantum device to slow down simulated chemical reaction 100 billion timesScientists at the University of Sydney have, for the first time, used a quantum computer to engineer and directly observe a process critical in chemical reactions by slowing it down by a factor of 100 billion times.
Scientists use quantum device to slow down simulated chemical reaction 100 billion timesScientists at the University of Sydney have, for the first time, used a quantum computer to engineer and directly observe a process critical in chemical reactions by slowing it down by a factor of 100 billion times.
Read more »