Nature research paper: Ancient gene linkages support ctenophores as sister to other animals
suggest that outgroup comparisons could be used to infer ancestral metazoan states and polarize changes within animals to address the sponge-sister versus ctenophore-sister debate. Yet, chromosome-scale genome sequences of the unicellular or colonial eukaryotic outgroups closest to animals have not been reported.
Here we show that conserved syntenies between animals and their closest unicellular relatives support ctenophores as the sister group to all other animals. Specifically, we find seven sets of genes for which ctenophores share ancestral metazoan gene linkages with one or more unicellular eukaryotes; and bilaterians, cnidarians, placozoans and sponges are united by shared derived patterns of synteny that arose by ancient interchromosomal translocations.
To examine conserved syntenies across animals, we traced the chromosomal distribution of orthologous genes among diverse metazoan lineages using previously and newly sequenced genomes (Fig.
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
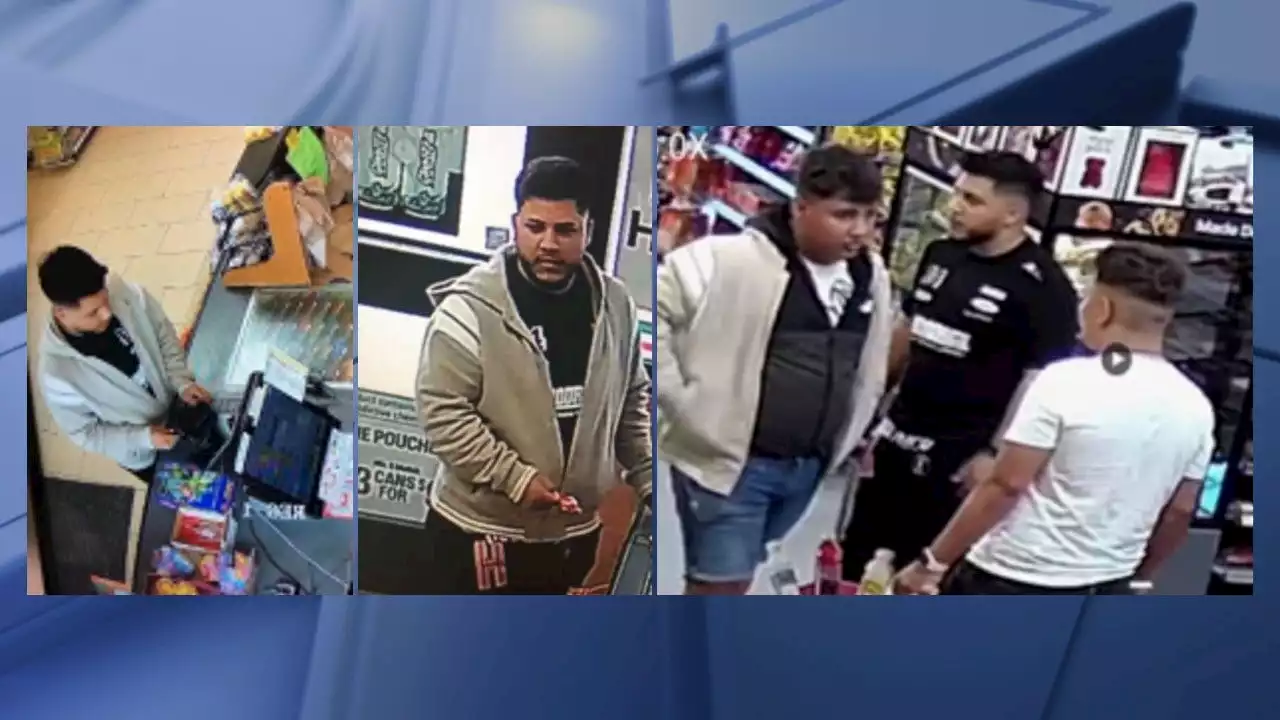 Suspects wanted for placing skimmers at Forney convenience storesForney police are searching for three men accused of installing credit card skimmers at multiple convenience stores in the city.
Suspects wanted for placing skimmers at Forney convenience storesForney police are searching for three men accused of installing credit card skimmers at multiple convenience stores in the city.
Read more »
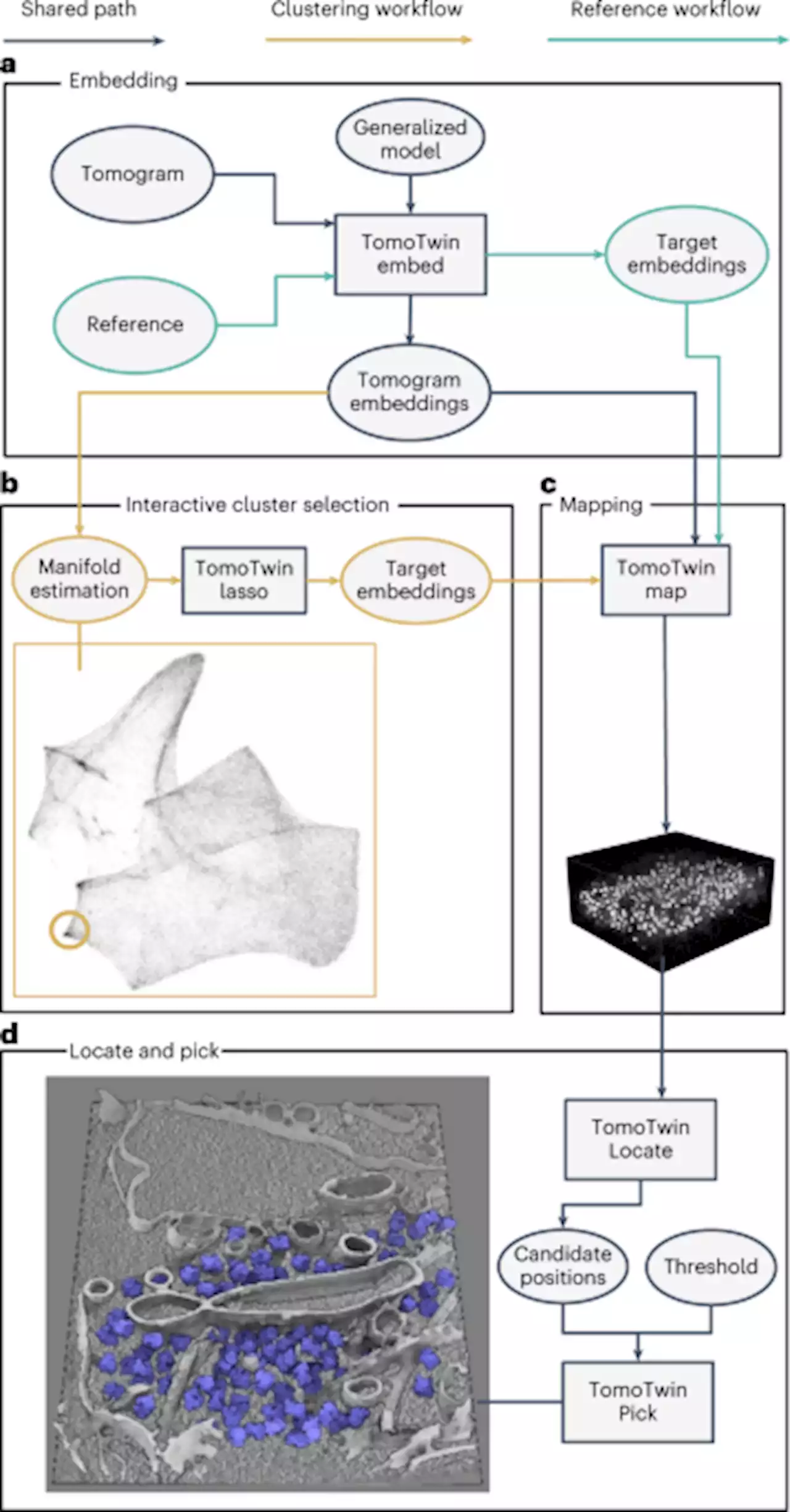 TomoTwin: generalized 3D localization of macromolecules in cryo-electron tomograms with structural data mining - Nature MethodsTomoTwin is a deep metric learning-based particle picking method for cryo-electron tomograms. TomoTwin obviates the need for annotating training data and retraining a picking model for each protein.
TomoTwin: generalized 3D localization of macromolecules in cryo-electron tomograms with structural data mining - Nature MethodsTomoTwin is a deep metric learning-based particle picking method for cryo-electron tomograms. TomoTwin obviates the need for annotating training data and retraining a picking model for each protein.
Read more »
Spectroscopic identification of water emission from a main-belt comet - NatureNature research paper: Spectroscopic identification of water emission from a main-belt comet
Read more »
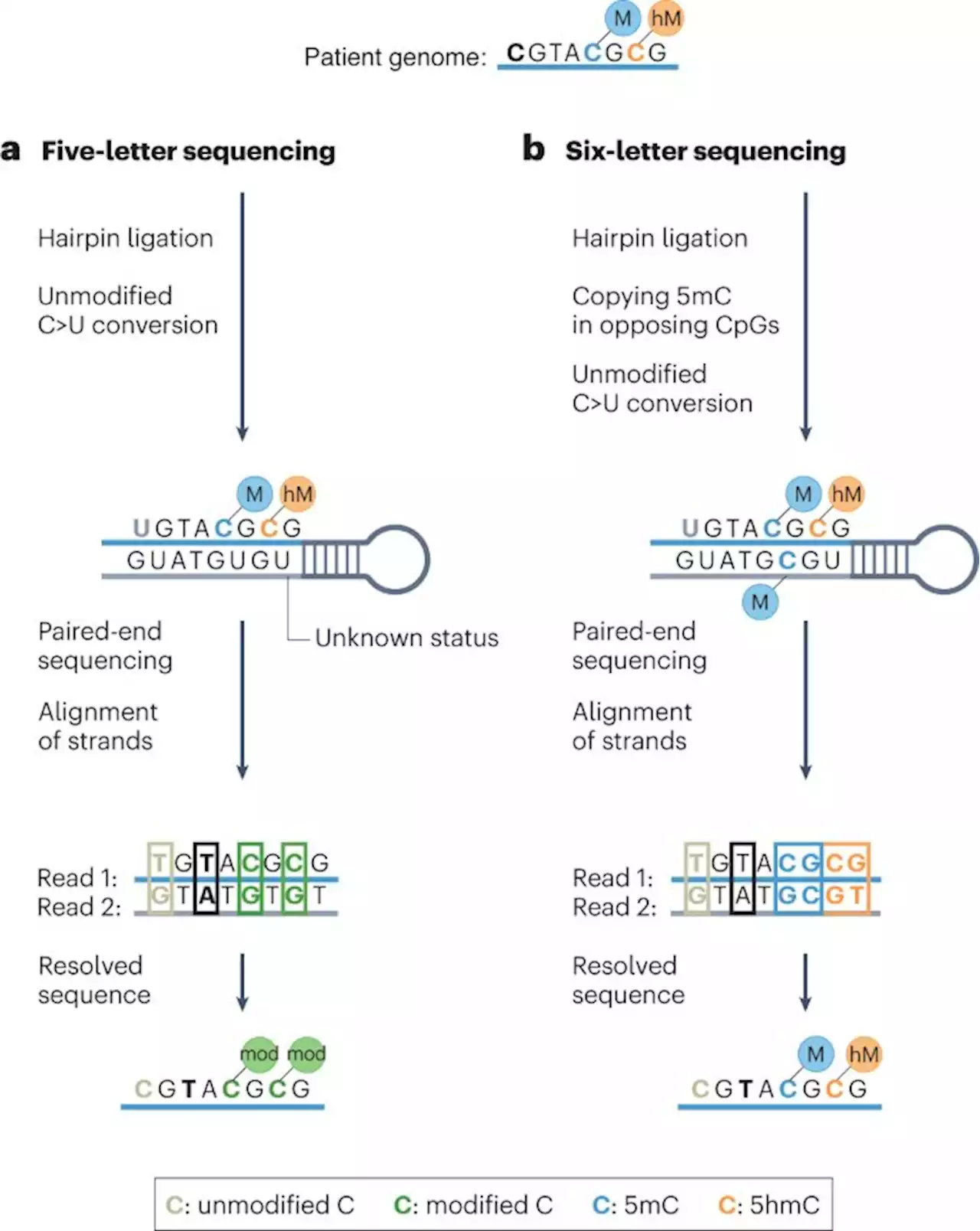 Speed reading the epigenome and genome - Nature BiotechnologyDual sequencing of the epigenome and genome could have broad implications in oncology, write James M. George & ArulChinnaiyan NBTNV
Speed reading the epigenome and genome - Nature BiotechnologyDual sequencing of the epigenome and genome could have broad implications in oncology, write James M. George & ArulChinnaiyan NBTNV
Read more »
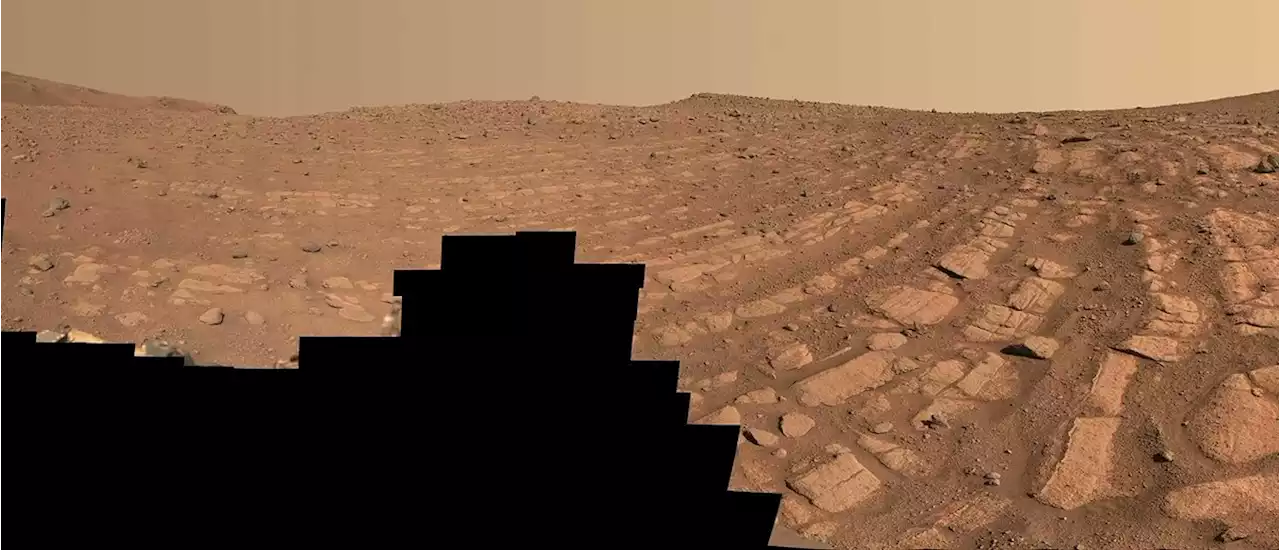 Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing RiverIn a first for Martian water science, NASA’s Perseverance rover has discovered geological evidence of a large, fast-moving river in Mars’ ancient past. The high-energy river once emptied into Jezero crater, which the rover has been exploring since early 2021, and is a totally different water system than anything seen previously on the red planet. … Continue reading 'Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing River'
Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing RiverIn a first for Martian water science, NASA’s Perseverance rover has discovered geological evidence of a large, fast-moving river in Mars’ ancient past. The high-energy river once emptied into Jezero crater, which the rover has been exploring since early 2021, and is a totally different water system than anything seen previously on the red planet. … Continue reading 'Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing River'
Read more »
