Space and astronomy news
An artist's depiction of the liquid silicate layer wrapped around the Martian core. Credit: IPGP-CNES.
It has long been believed that Mars once had a global magnetic field like Earth does, but somehow the iron-core dynamo that generated it must have shut down billions of years ago. “The blanket not only insulates the heat coming from the core and prevents the core from cooling, but also concentrates radioactive elements whose decay generates heat,” said Vedran Lekic, a professor at the University of Maryland and co-author of a“And when that happens, the core is likely to be unable to produce the convective motions that would create a magnetic field—which can explain why Mars currently doesn’t have an active magnetic field around it.
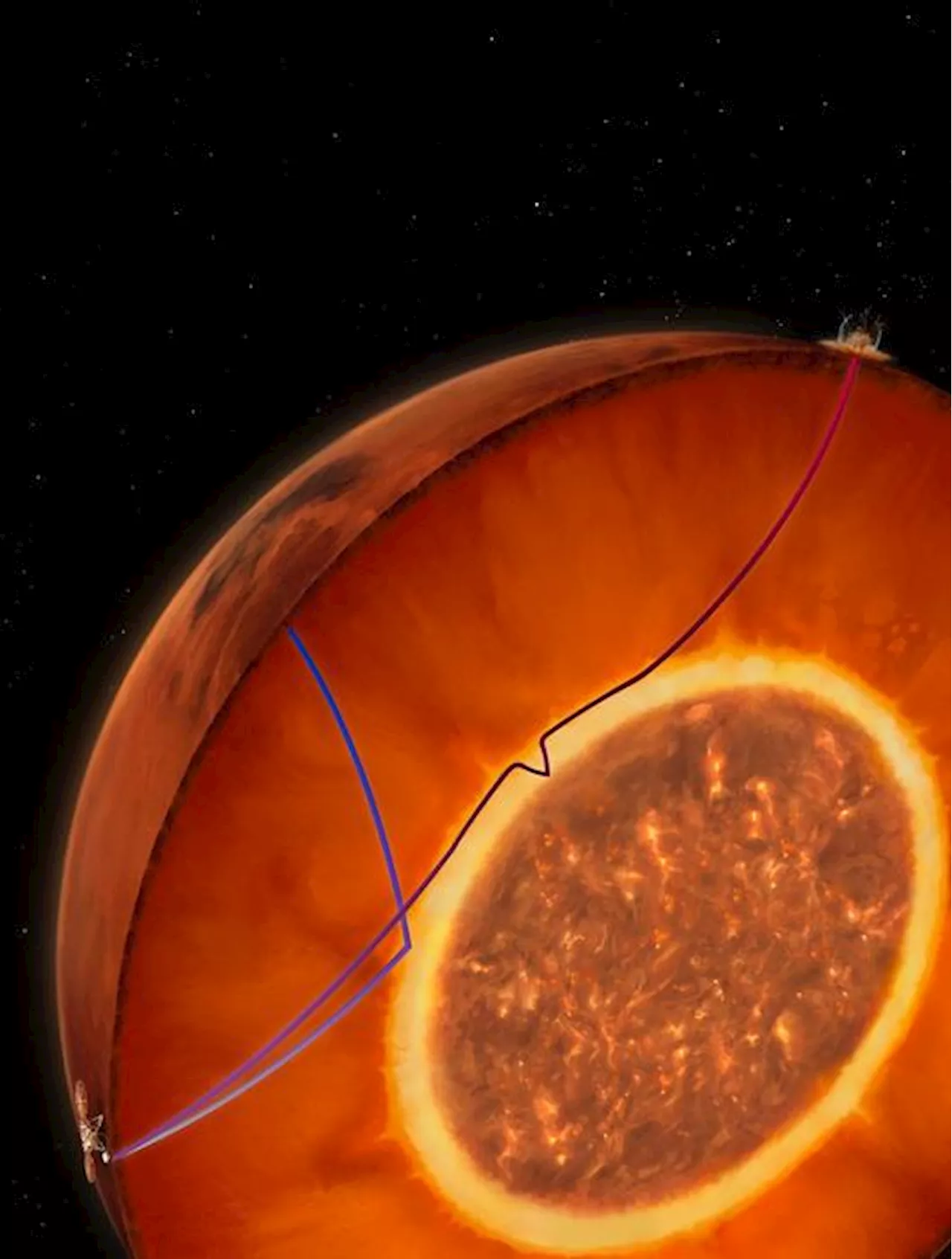
Without the protection a magnetic field provided, Mars’ atmosphere was stripped, and eventually, any water on the surface – even oceans – would have evaporated as water vapor in the atmosphere was lost to space, making it incapable of sustaining life.NASA’s InSight mission deployed the first seismometer on the surface of Mars.
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New study finds Mars's liquid iron core is smaller and denser than previously thoughtFor four years, NASA's InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analyzed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet's internal structure.
New study finds Mars's liquid iron core is smaller and denser than previously thoughtFor four years, NASA's InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analyzed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet's internal structure.
Read more »
 Swell shakes up liquid staking market with new stETH vaultstETH holders can now deposit in the Super swETH vault to earn supercharged rewards from Pearls and redirected DAO commission, and help diversify the liquid staking market
Swell shakes up liquid staking market with new stETH vaultstETH holders can now deposit in the Super swETH vault to earn supercharged rewards from Pearls and redirected DAO commission, and help diversify the liquid staking market
Read more »
 Omni Liquid Staking DApp - A New Experience in the Era of Chain AbstractionWith the development of a multi-chain ecosystem and the prosperity of Ethereum L2 solutions, users and developers have more choices. However, this also brings about the issues of fragmented user experience and liquidity.
Omni Liquid Staking DApp - A New Experience in the Era of Chain AbstractionWith the development of a multi-chain ecosystem and the prosperity of Ethereum L2 solutions, users and developers have more choices. However, this also brings about the issues of fragmented user experience and liquidity.
Read more »
 Large Investors Choose CryptoStake: a Swiss-Based Staking Hub Where Security Meets Regulatory ComplianceCryptoStake, novel easy-to-use staking protocol, introduces secure and profitable alternative for liquid staking platforms
Large Investors Choose CryptoStake: a Swiss-Based Staking Hub Where Security Meets Regulatory ComplianceCryptoStake, novel easy-to-use staking protocol, introduces secure and profitable alternative for liquid staking platforms
Read more »
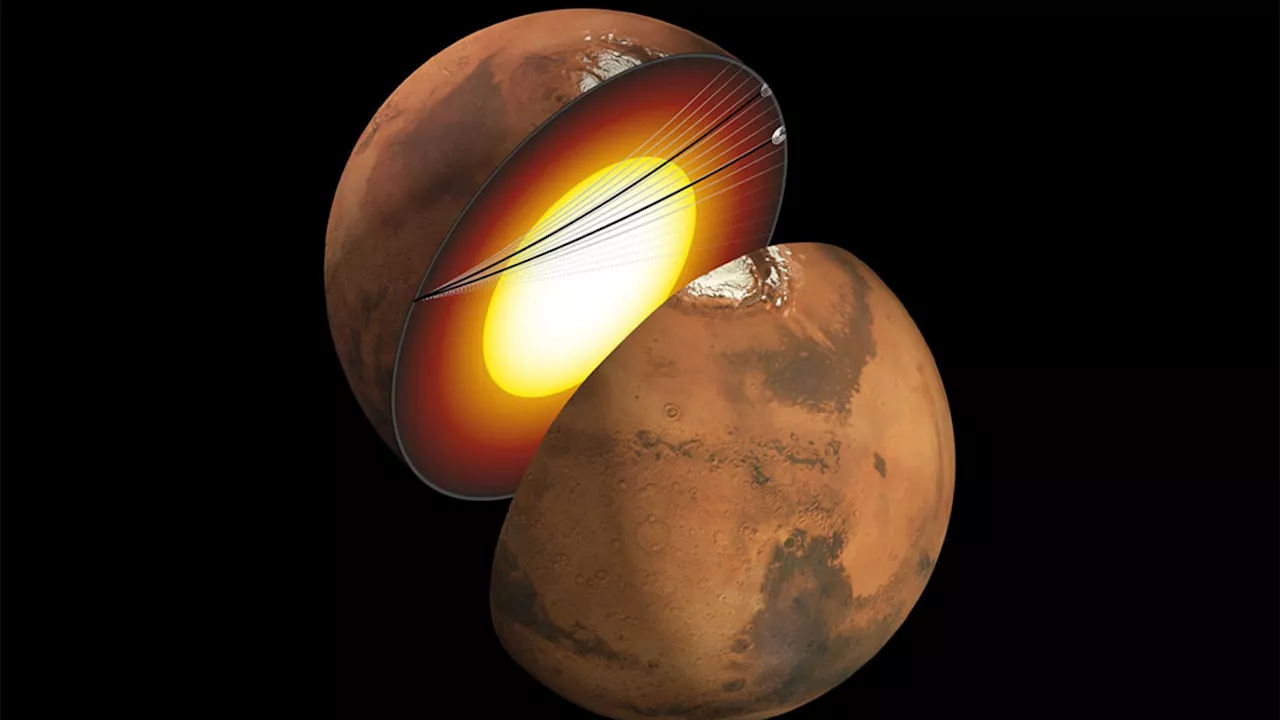 Scientists discover a 160-mile-thick layer of molten silicates on MarsInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
Scientists discover a 160-mile-thick layer of molten silicates on MarsInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
Read more »
 Curiosity rover discovers new evidence Mars once had 'right conditions' for lifeKeith Cooper is a freelance science journalist and editor in the United Kingdom, and has a degree in physics and astrophysics from the University of Manchester.
Curiosity rover discovers new evidence Mars once had 'right conditions' for lifeKeith Cooper is a freelance science journalist and editor in the United Kingdom, and has a degree in physics and astrophysics from the University of Manchester.
Read more »
