The successful transfer of a gene that produces HMW-HA paves the way for improving the health and lifespan of humans, too. In a groundbreaking endeavor, scientists at the University of Rochester have successfully transferred a longevity gene from naked mole rats to mice, leading to enhanced health
Researchers successfully transferred a longevity gene from naked mole rats to mice, leading to enhanced health and increased lifespan. Naked mole rats, noted for their resistance to age-related diseases, have a gene that produces high molecular weight hyaluronic acid , which when introduced to mice, demonstrated potential anti-aging benefits.
“Our study provides a proof of principle that unique longevity mechanisms that evolved in long-lived mammaliancan be exported to improve the lifespans of other mammals,” says Vera Gorbunova, the Doris Johns Cherry Professor of biology and medicine at Rochester. The researchers previously discovered that HMW-HA is one mechanism responsible for naked mole rats’ unusual resistance to cancer. Compared to mice and humans, naked mole rats have about ten times more HMW-HA in their bodies. When the researchers removed HMW-HA from naked mole rat cells, the cells were more likely to form tumors.
While more research is needed on exactly why HMW-HA has such beneficial effects, the researchers believe it is due to HMW-HA’s ability to directly regulate the immune system.The findings open new possibilities for exploring how HMW-HA could also be used to improve lifespan and reduce inflammation-related diseases in humans.
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
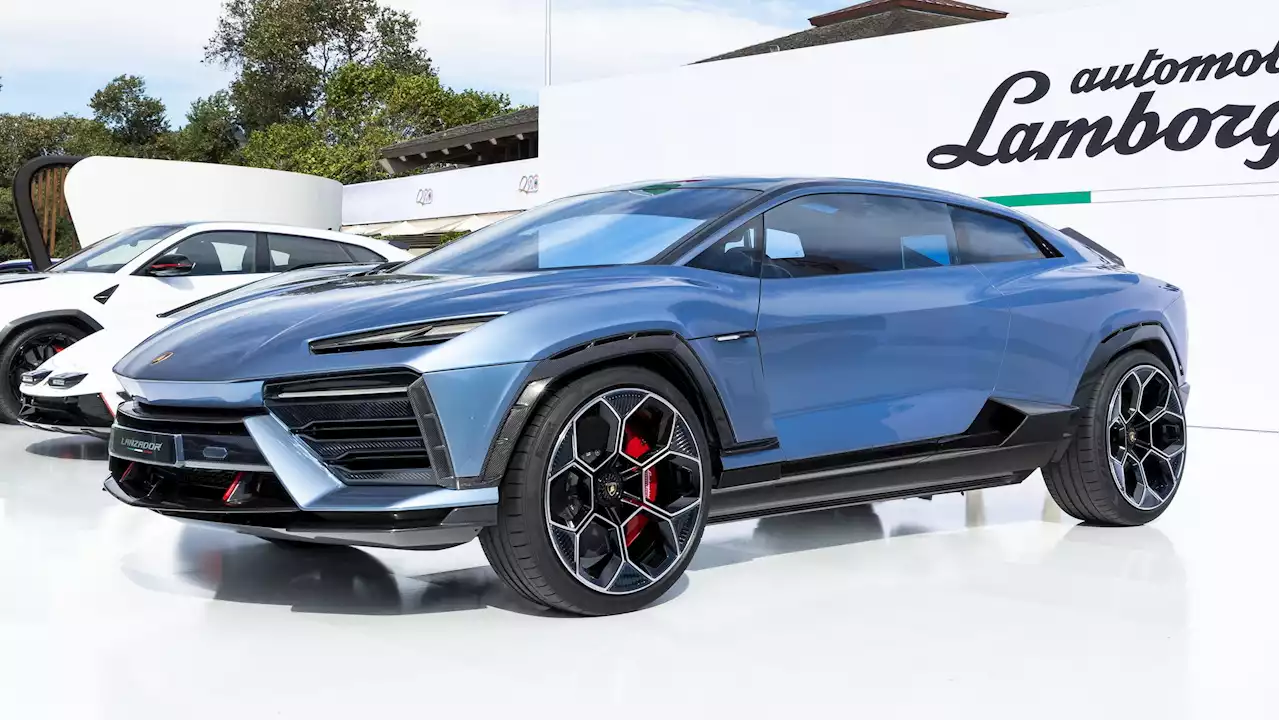 The Lanzador Is A New Kind Of Lamborghini, Looking For A New Kind Of CustomerElectrification means a bit of an existential crisis for Lamborghini, but the Lanzador concept is the first step in answering what the brand looks like without a V12 to lean on
The Lanzador Is A New Kind Of Lamborghini, Looking For A New Kind Of CustomerElectrification means a bit of an existential crisis for Lamborghini, but the Lanzador concept is the first step in answering what the brand looks like without a V12 to lean on
Read more »
 Brighter and More Efficient Next-Gen LEDs: Stanford Breakthrough Comes at a CostA Molecular Additive Enhances Next-Gen LEDs – But Shortens Their Lifespans By tinkering with the material makeup of perovskite LEDs, a cheaper and more easily made type of LED, Stanford researchers achieved leaps in brightness and efficiency – but saw their lights give out after a few minutes of us
Brighter and More Efficient Next-Gen LEDs: Stanford Breakthrough Comes at a CostA Molecular Additive Enhances Next-Gen LEDs – But Shortens Their Lifespans By tinkering with the material makeup of perovskite LEDs, a cheaper and more easily made type of LED, Stanford researchers achieved leaps in brightness and efficiency – but saw their lights give out after a few minutes of us
Read more »
 Genetic Breakthrough: Scientists Induce Asexual Reproduction in Fruit FliesResearchers have successfully induced asexual reproduction in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, an organism that typically reproduces sexually. For the first time, scientists have induced asexual reproduction in an animal that usually reproduces sexually: the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaste
Genetic Breakthrough: Scientists Induce Asexual Reproduction in Fruit FliesResearchers have successfully induced asexual reproduction in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, an organism that typically reproduces sexually. For the first time, scientists have induced asexual reproduction in an animal that usually reproduces sexually: the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaste
Read more »
 Breakthrough in beta-lactam synthesis using nickel catalystsResearchers have made a significant breakthrough in the field of asymmetric synthesis of beta-lactams, which are prominent in bioactive compounds. Their innovative approach employs nickel and hydrocarbon sources that are abundant on Earth to access value-added beta-lactam products. The employment of nickel-hydride catalysis and alkenyl dioxazolone derivatives gives rise to the selective formation of four-membered lactam products.
Breakthrough in beta-lactam synthesis using nickel catalystsResearchers have made a significant breakthrough in the field of asymmetric synthesis of beta-lactams, which are prominent in bioactive compounds. Their innovative approach employs nickel and hydrocarbon sources that are abundant on Earth to access value-added beta-lactam products. The employment of nickel-hydride catalysis and alkenyl dioxazolone derivatives gives rise to the selective formation of four-membered lactam products.
Read more »
 New on Netflix: September 2023's Best New Movies & ShowsHead back to school next month with new seasons of 'Sex Education', 'Love Is Blind', and many more.
New on Netflix: September 2023's Best New Movies & ShowsHead back to school next month with new seasons of 'Sex Education', 'Love Is Blind', and many more.
Read more »
 Novak Djokovic Returns to New York With a New Rival in His SightsAfter a career spent chasing Federer and Nadal, the 23-time major champion is settling into a rivalry with Carlos Alcaraz.
Novak Djokovic Returns to New York With a New Rival in His SightsAfter a career spent chasing Federer and Nadal, the 23-time major champion is settling into a rivalry with Carlos Alcaraz.
Read more »
