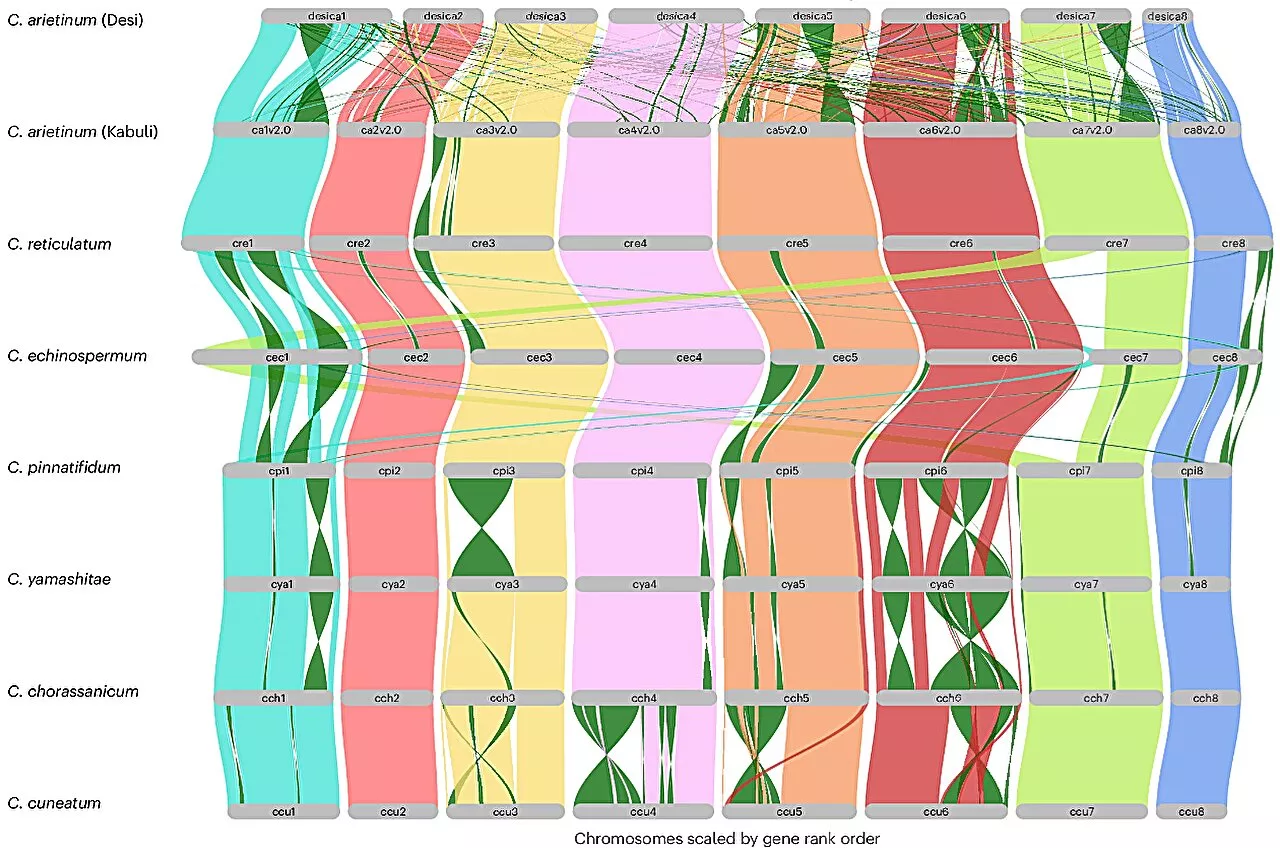
A new study has revealed the potential of using wild crop relatives for chickpea improvement, paving the way for more advanced crops and greater global food security.
Researchers make better chickpeas possible by harnessing genetic traits of wild cousins retrieved 24 May 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-05-chickpeas-harnessing-genetic-traits-wild.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.19 hours agoUse this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers unveil PI3K enzyme's dual accelerator and brake mechanismsA group of researchers have expanded conventional knowledge on a critical enzyme that controls cell migration. In a publication in the journal Nature Communications, they reported that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) not only acts as an accelerator to prompt cell motility, but it also has a built-in brake mechanism that impedes migration.
Researchers unveil PI3K enzyme's dual accelerator and brake mechanismsA group of researchers have expanded conventional knowledge on a critical enzyme that controls cell migration. In a publication in the journal Nature Communications, they reported that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) not only acts as an accelerator to prompt cell motility, but it also has a built-in brake mechanism that impedes migration.
Read more »
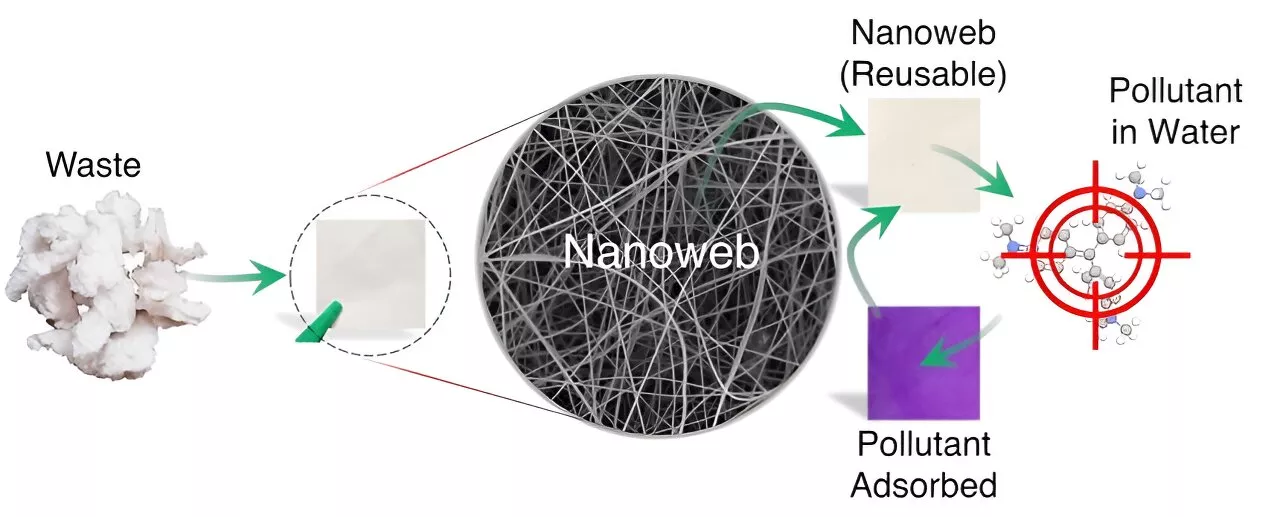 Nanofibers rid water of hazardous dyes: Researchers develop efficient filters based on cellulose wasteUsing waste to purify water may sound counterintuitive. But at TU Wien, this is exactly what has now been achieved. Researchers have developed a special nanostructure to filter a widespread class of harmful dyes from water.
Nanofibers rid water of hazardous dyes: Researchers develop efficient filters based on cellulose wasteUsing waste to purify water may sound counterintuitive. But at TU Wien, this is exactly what has now been achieved. Researchers have developed a special nanostructure to filter a widespread class of harmful dyes from water.
Read more »
 Researchers create first artificial, modifiable cells with programmable DNAThe achievement holds significant promise for advancements in regenerative medicine, drug delivery methods, and diagnostic technologies.
Researchers create first artificial, modifiable cells with programmable DNAThe achievement holds significant promise for advancements in regenerative medicine, drug delivery methods, and diagnostic technologies.
Read more »
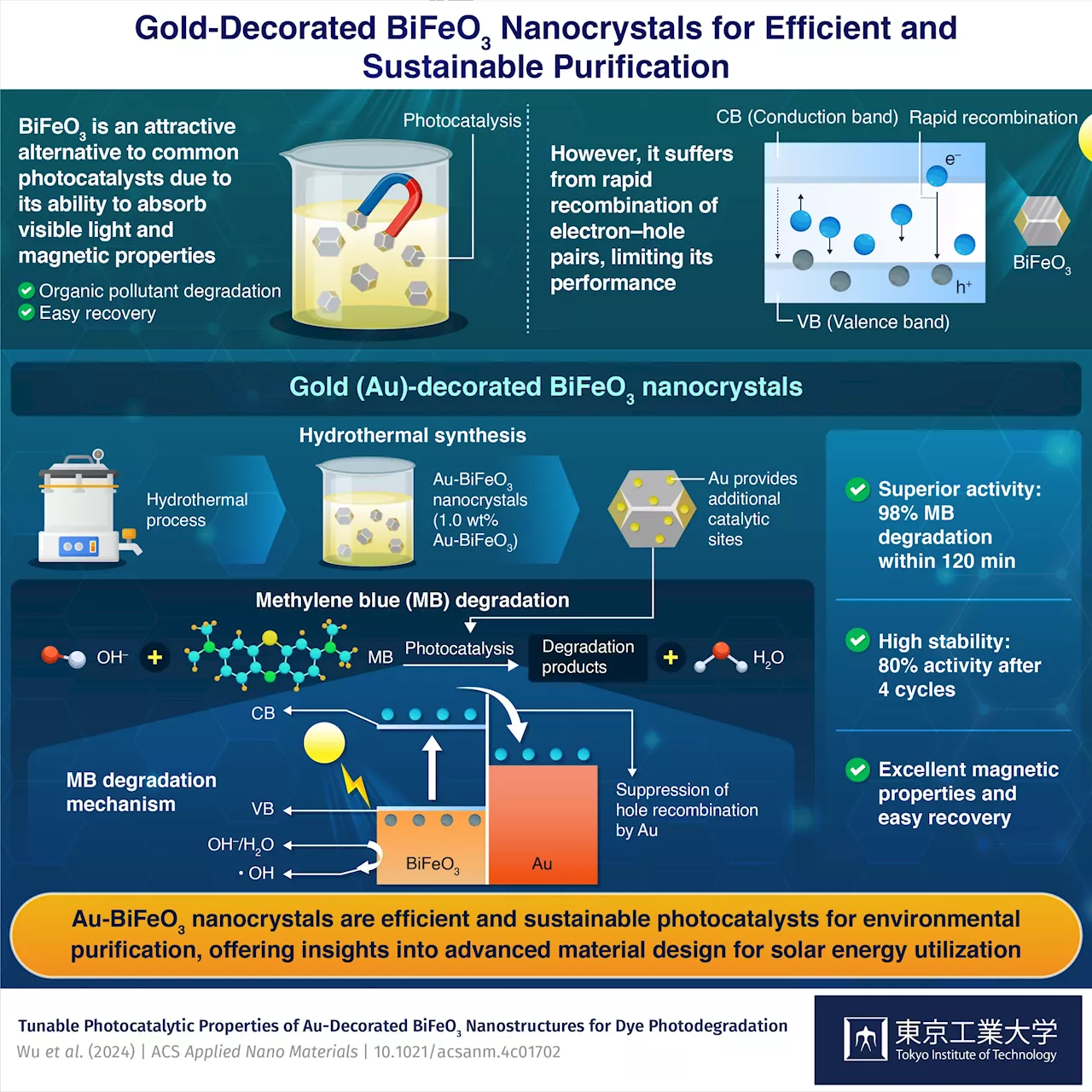 Researchers create nanostructures for efficient and sustainable degradation of pollutantsThe need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing to their potential in mitigating pollutants and harnessing solar energy efficiently.
Researchers create nanostructures for efficient and sustainable degradation of pollutantsThe need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing to their potential in mitigating pollutants and harnessing solar energy efficiently.
Read more »
 Researchers uncover 'parallel universe' in tomato geneticsIn a paper appearing in Science Advances, Michigan State University researchers have unraveled a surprising genetic mystery centered on sugars found in what gardeners know as 'tomato tar.'
Researchers uncover 'parallel universe' in tomato geneticsIn a paper appearing in Science Advances, Michigan State University researchers have unraveled a surprising genetic mystery centered on sugars found in what gardeners know as 'tomato tar.'
Read more »
 Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth's magnetic fieldA new study has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth's magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today.
Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth's magnetic fieldA new study has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth's magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today.
Read more »