Researchers say their findings are consistent with sleep-deprived investors mispricing and revisiting relevant information.
The spring clock change significantly affects how investors respond to companies that reveal unexpected levels of earnings, new research shows.
Researchers say their findings are consistent with sleep-deprived investors mispricing and subsequently revisiting relevant information. The research team hopes the study – published in The European Journal of Finance – will deepen understanding of the effects of sleep deprivation on financial markets.
These high levels of returns are consistent with investors revisiting – and reversing – their initial underreaction to earnings surprises
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
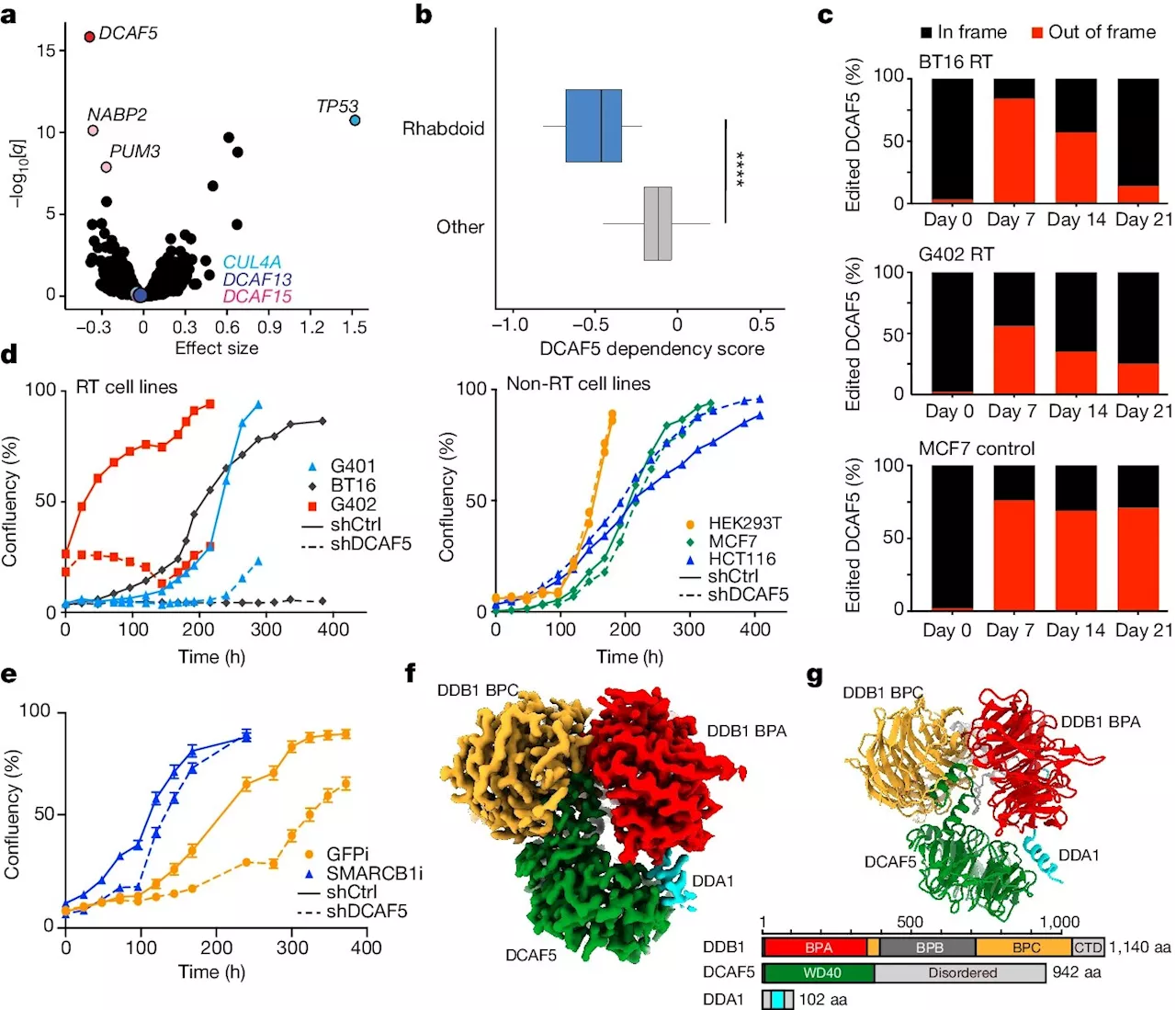 Researchers turn back the clock on cancer cells to offer new treatment paradigmSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists reversed an aggressive cancer, reverting malignant cells towards a more normal state. Rhabdoid tumors are an aggressive cancer which is missing a key tumor suppressor protein.
Researchers turn back the clock on cancer cells to offer new treatment paradigmSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists reversed an aggressive cancer, reverting malignant cells towards a more normal state. Rhabdoid tumors are an aggressive cancer which is missing a key tumor suppressor protein.
Read more »
 Researchers report rare but persistent false positives on COVID-19 home antigen testsUMass Chan Medical School researchers have documented a phenomenon that had confounded clinicians: Some people persistently test positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, on rapid home antigen tests despite obtaining concurrent negative PCR tests.
Researchers report rare but persistent false positives on COVID-19 home antigen testsUMass Chan Medical School researchers have documented a phenomenon that had confounded clinicians: Some people persistently test positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, on rapid home antigen tests despite obtaining concurrent negative PCR tests.
Read more »
 Researchers report on the effectiveness of skin biopsy to detect Parkinson's and related neurodegenerative diseasesIn a paper published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), neurologists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) showed that a simple skin biopsy test detects an abnormal form of alpha-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease and the subgroup of neurodegenerative disorders known as synucleinopathies,...
Researchers report on the effectiveness of skin biopsy to detect Parkinson's and related neurodegenerative diseasesIn a paper published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), neurologists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) showed that a simple skin biopsy test detects an abnormal form of alpha-synuclein, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson's disease and the subgroup of neurodegenerative disorders known as synucleinopathies,...
Read more »
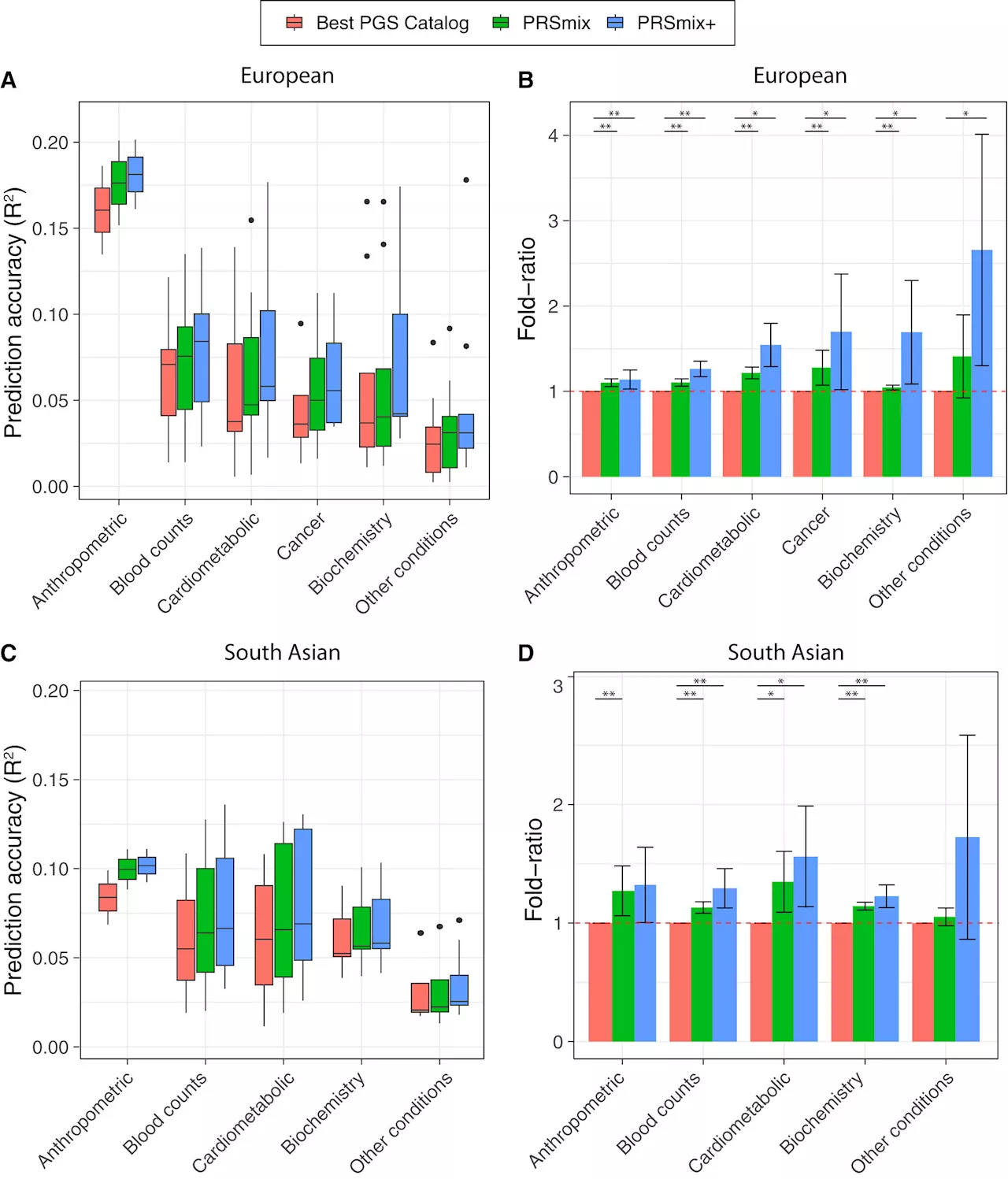 Researchers roll out a more accurate way to estimate genetic risks of diseaseResearchers have developed statistical tools called polygenic risk scores (PRSs) that can estimate individuals' risk for certain diseases with strong genetic components, such as heart disease or diabetes. However, the data on which PRSs are built is often limited in diversity and scope.
Researchers roll out a more accurate way to estimate genetic risks of diseaseResearchers have developed statistical tools called polygenic risk scores (PRSs) that can estimate individuals' risk for certain diseases with strong genetic components, such as heart disease or diabetes. However, the data on which PRSs are built is often limited in diversity and scope.
Read more »
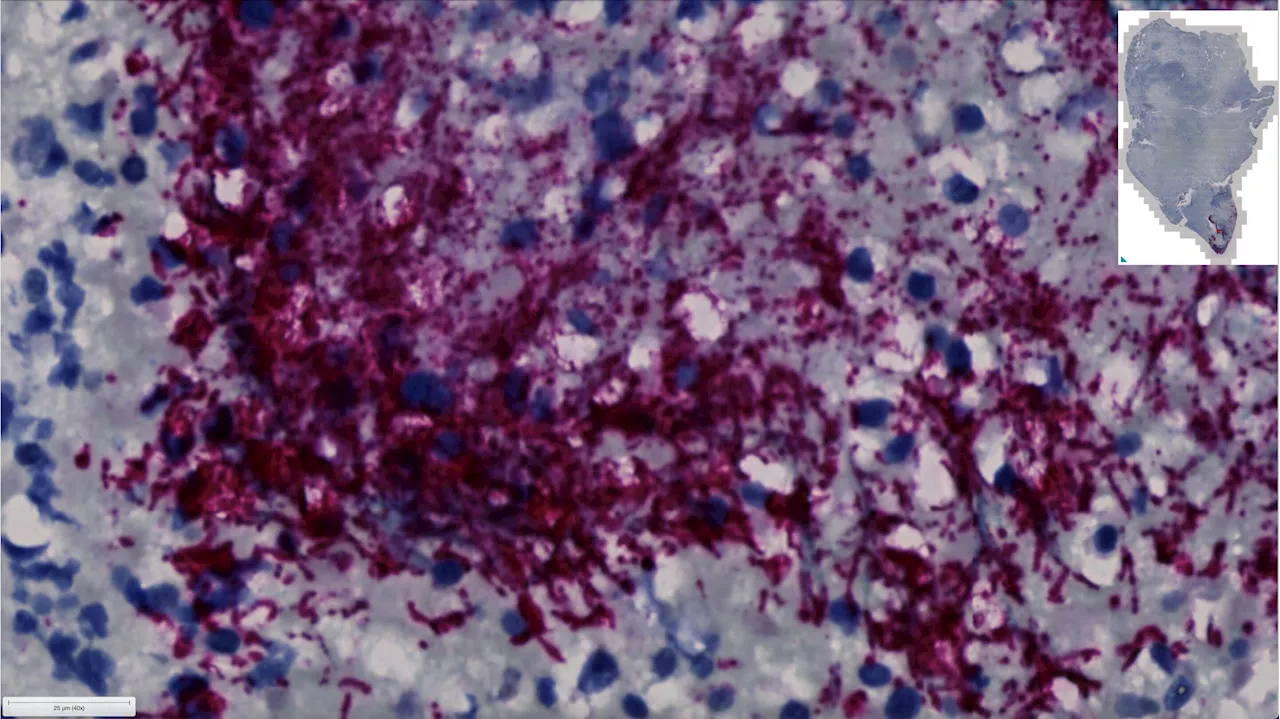 Bacteria subtype linked to growth in up to 50% of human colorectal cancers, researchers reportResearchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center have found that a specific subtype of a microbe commonly found in the mouth is able to travel to the gut and grow within colorectal cancer tumors. This microbe is also a culprit for driving cancer progression and leads to poorer patient outcomes after cancer treatment.
Bacteria subtype linked to growth in up to 50% of human colorectal cancers, researchers reportResearchers at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center have found that a specific subtype of a microbe commonly found in the mouth is able to travel to the gut and grow within colorectal cancer tumors. This microbe is also a culprit for driving cancer progression and leads to poorer patient outcomes after cancer treatment.
Read more »
 Researchers develop early detection method for rare Borna virusResearchers at Augsburg University Medicine have discovered a possible early detection method of the rare Borna virus. Their results have been published in The Lancet. In humans the virus triggers inflammation in the brain which is almost always deadly and is transmitted to humans by shrews.
Researchers develop early detection method for rare Borna virusResearchers at Augsburg University Medicine have discovered a possible early detection method of the rare Borna virus. Their results have been published in The Lancet. In humans the virus triggers inflammation in the brain which is almost always deadly and is transmitted to humans by shrews.
Read more »
