Researchers revealed the importance of the transmission of epigenetic information through cell division for embryonic stem cells functionality. This has broad implications for aging, cancer, and regenerative medicine.
each type of cell expresses and has the potential to communicate this information to its daughter cells.
"Understanding the layers which control epigenetic memory could be a key to aging and cancer avoidance as well as facilitating more efficient cellular reprogramming and trans-differentiation for applications regenerative medicine," says Joshua Brickman, Professor at Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Stem Cell Medicine, reNEW Copenhagen.
"By using this information, we were able to manipulate the machinery to create mouse embryotic stem cells, where one daughter DNA strand lacks the transmitted histones with the memory signal while the other gets it all," says postdoc at Novo Nordisk Foundation for Protein Research Alva Biran and co first author of the study.
, which the investigator found to enable the balanced inheritance of functional properties associated with cell identity.
Singapore Latest News, Singapore Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Lung conditions will be made worse by climate change, say researchersRespiratory experts are calling on governments to reduce emissions and improve air quality using the same policies.
Lung conditions will be made worse by climate change, say researchersRespiratory experts are calling on governments to reduce emissions and improve air quality using the same policies.
Read more »
 Lung conditions will be made worse by climate change, say researchersRespiratory experts are calling on governments to reduce emissions and improve air quality using the same policies.
Lung conditions will be made worse by climate change, say researchersRespiratory experts are calling on governments to reduce emissions and improve air quality using the same policies.
Read more »
 Researchers develop tools to identify patients at risk of medication harmA University of Queensland research collaboration will look at reducing the risk of harm from medication for inpatients and those leaving hospital to return home.
Researchers develop tools to identify patients at risk of medication harmA University of Queensland research collaboration will look at reducing the risk of harm from medication for inpatients and those leaving hospital to return home.
Read more »
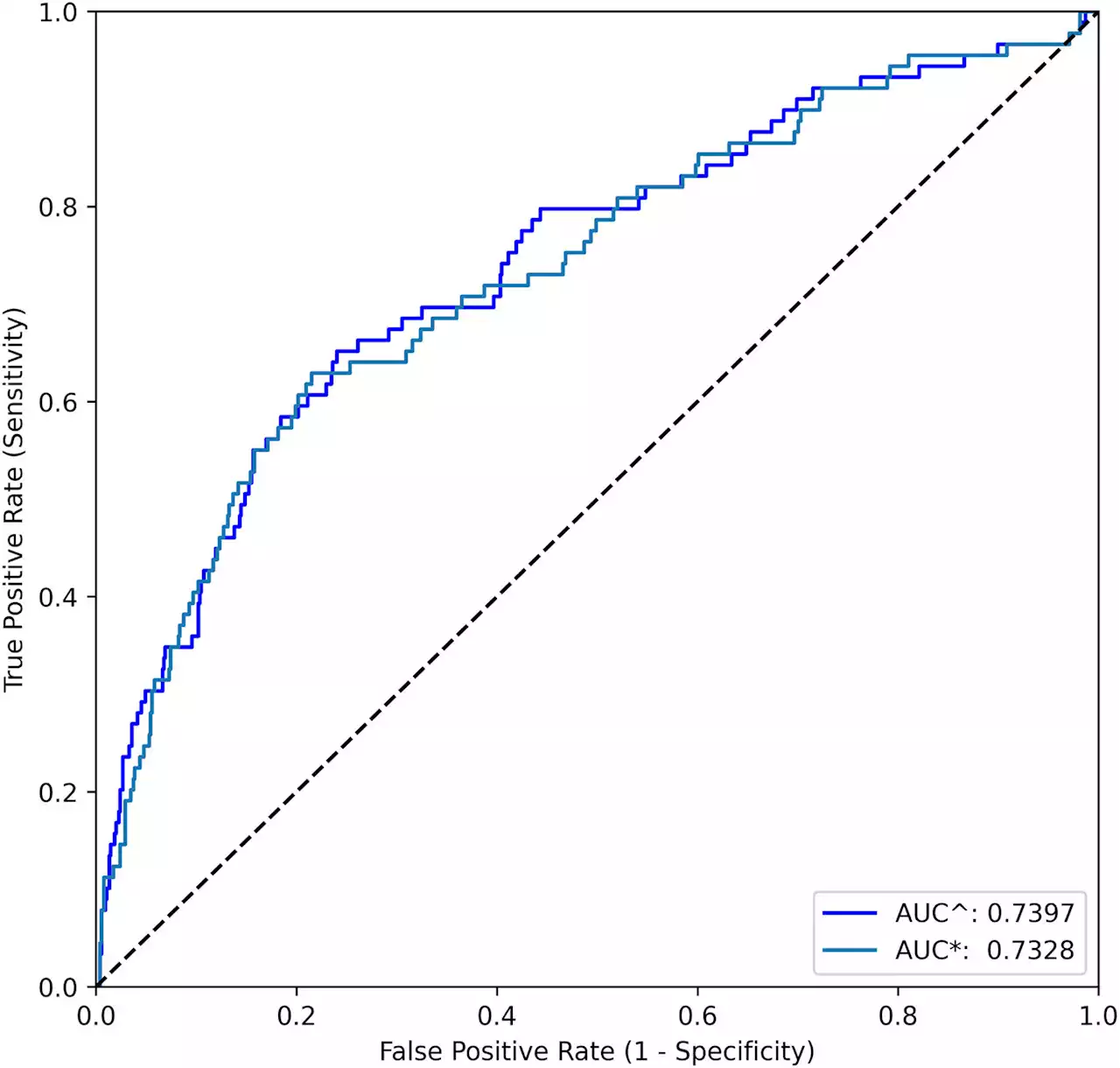 Researchers design machine learning models to better predict adolescent suicide and self-harm riskArtificial intelligence can help to identify risk factors for suicide and self-harm, according to new research from UNSW Sydney.
Researchers design machine learning models to better predict adolescent suicide and self-harm riskArtificial intelligence can help to identify risk factors for suicide and self-harm, according to new research from UNSW Sydney.
Read more »
 Growing evidence supports the protein leverage hypothesis as a significant mechanism driving obesity, study findsHumans, like many other species, regulate protein intake more strongly than any other dietary component and so if protein is diluted there is a compensatory increase in food intake. The hypothesis proposes that the dilution of protein in modern-day diets by fat and carbohydrate-rich processed foods is driving increased energy intake as the body seeks to satisfy its natural protein drive—eating unnecessary calories until it does so.
Growing evidence supports the protein leverage hypothesis as a significant mechanism driving obesity, study findsHumans, like many other species, regulate protein intake more strongly than any other dietary component and so if protein is diluted there is a compensatory increase in food intake. The hypothesis proposes that the dilution of protein in modern-day diets by fat and carbohydrate-rich processed foods is driving increased energy intake as the body seeks to satisfy its natural protein drive—eating unnecessary calories until it does so.
Read more »
